Introduction to Clustering...
It is basically a type of unsupervised learning method . An unsupervised learning method is a method in which we draw references
from datasets consisting of input data without labelled responses. Generally, it is used as a process to find meaningful structure,
explanatory underlying processes, generative features, and groupings inherent in a set of examples.
Clustering is the task of dividing the population or data points into a number of groups such that data points in the same groups are more
similar to other data points in the same group and dissimilar to the data points in other groups. It is basically a collection of objects
on the basis of similarity and dissimilarity between them.
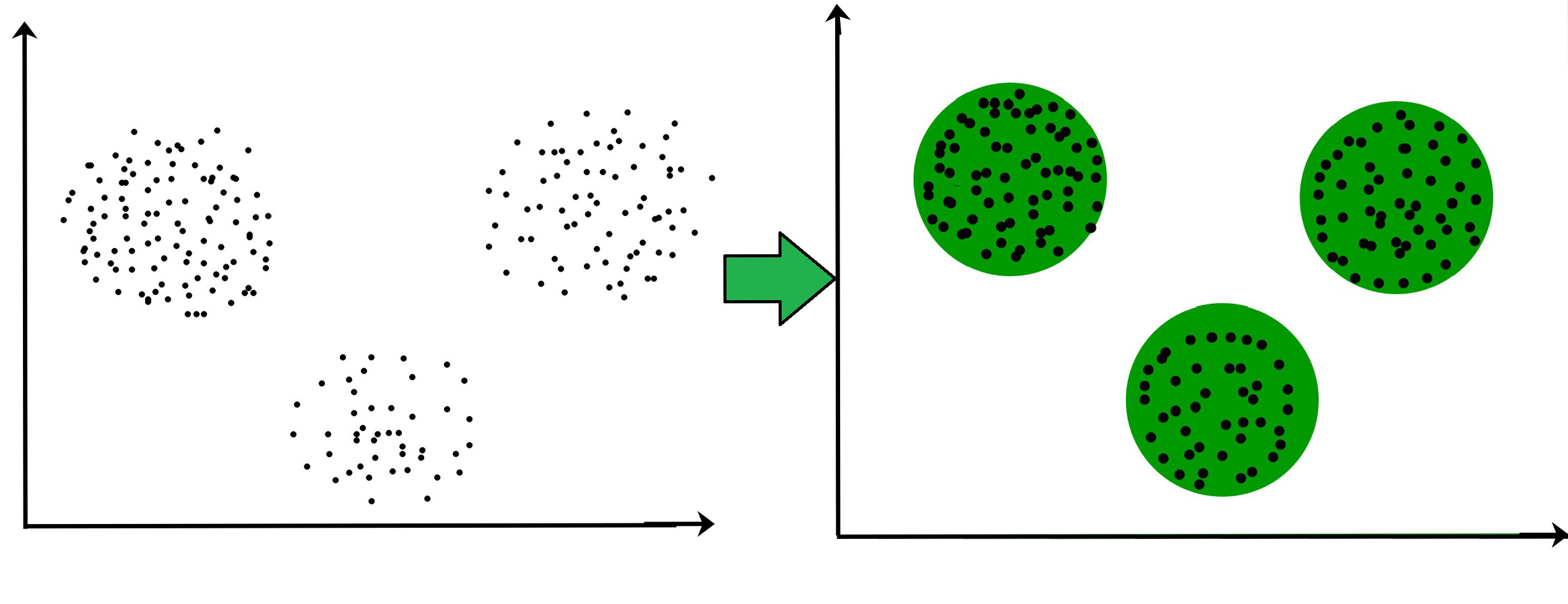
For example– The data points in the graph below clustered together can be classified into one single group. We can distinguish the clusters,
and we can identify that there are 3 clusters in the below picture.
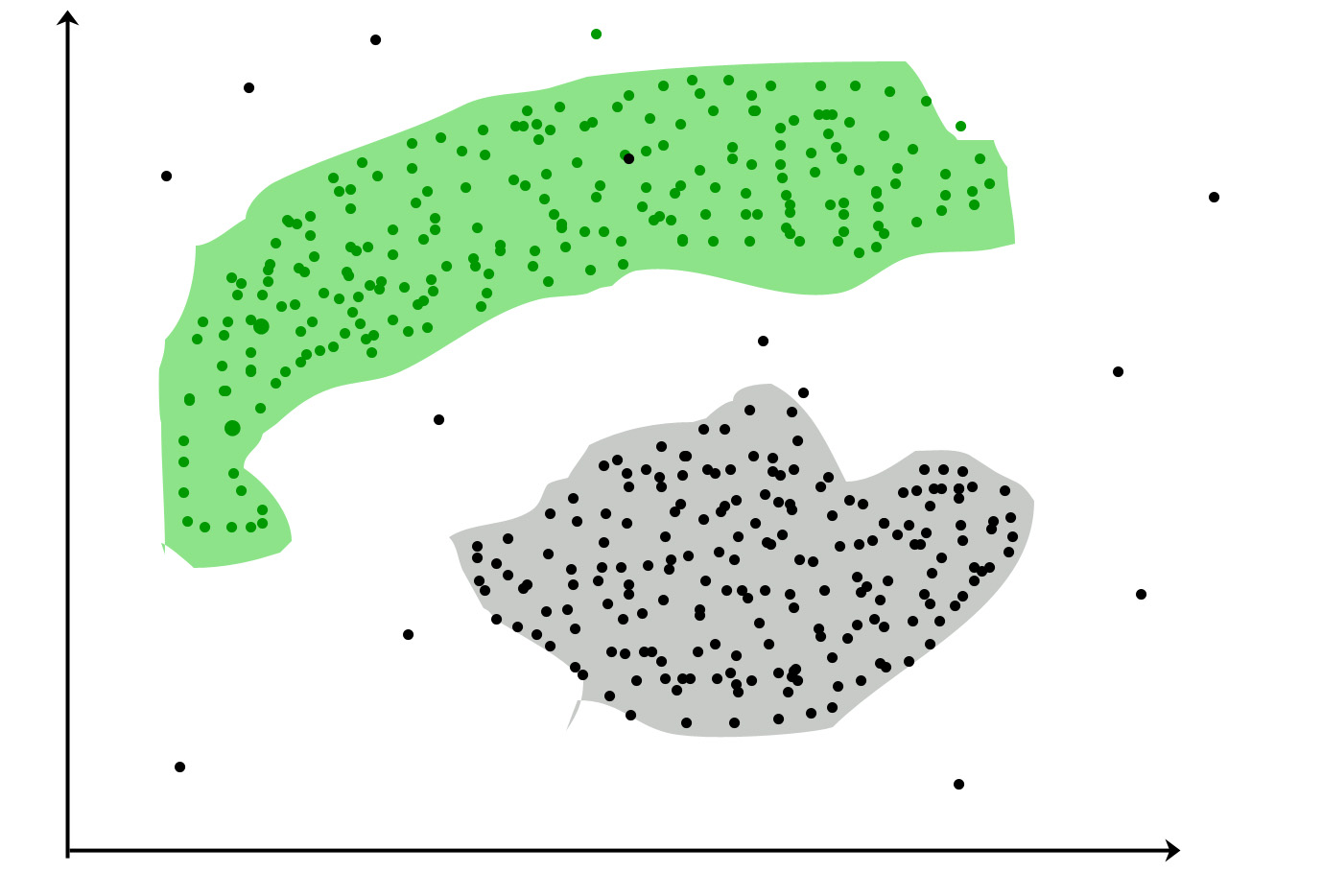
It is not necessary for clusters to be a spherical. Such as :
DBSCAN: Density-based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise
These data points are clustered by using the basic concept that the data point lies within the given constraint from the cluster centre.
Various distance methods and techniques are used for calculation of the outliers.
Why Clustering ?
Clustering is very much important as it determines the intrinsic grouping among the unlabeled data present. There are no criteria for a good clustering.
It depends on the user, what is the criteria they may use which satisfy their need. For instance, we could be interested in finding representatives
for homogeneous groups (data reduction), in finding “natural clusters” and describe their unknown properties (“natural” data types), in finding
useful and suitable groupings (“useful” data classes) or in finding unusual data objects (outlier detection). This algorithm must make some
assumptions which constitute the similarity of points and each assumption make different and equally valid clusters.
Clustering Methods :
1. Density-Based Methods : These methods consider the clusters as the dense region having some similarity and different from the lower dense region
of the space. These methods have good accuracy and ability to merge two clusters.Examples are DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with
Noise) , OPTICS (Ordering Points to Identify Clustering Structure) etc.
2. Hierarchical Based Methods : The clusters formed in this method forms a tree-type structure based on the hierarchy. New clusters are formed
using the previously formed one. It is divided into two category --
Agglomerative (bottom up approach) or, hierarchical agglomerative clustering (HAC)
Divisive (top down approach)
examples CURE (Clustering Using Representatives), BIRCH (Balanced Iterative Reducing Clustering and using Hierarchies) etc.
3. Partitioning Methods : These methods partition the objects into k clusters and each partition forms one cluster. This method is used
to optimize an objective criterion similarity function such as when the distance is a major parameter example: K-means, CLARANS (Clustering Large
Applications based upon Randomized Search) etc.
4. Grid-based Methods : In this method the data space is formulated into a finite number of cells that form a grid-like structure. All the
clustering operation done on these grids are fast and independent of the number of data objects examples STING (Statistical Information Grid), wave
cluster, CLIQUE (CLustering In Quest) etc.
Clustering Algorithms :
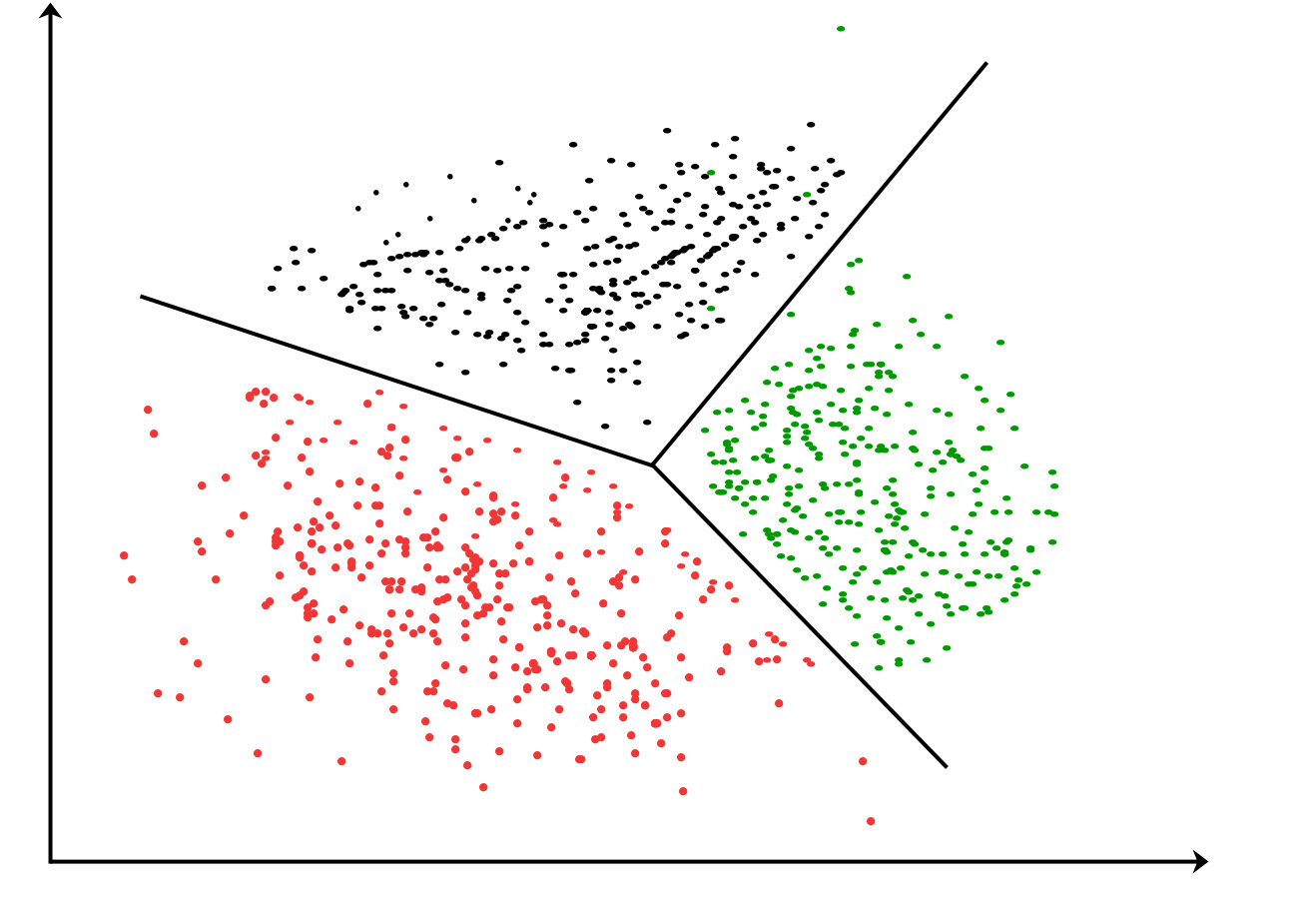
K-means clustering algorithm – It is the simplest unsupervised learning algorithm that solves clustering problem.K-means algorithm
partition n observations into k clusters where each observation belongs to the cluster with the nearest mean serving as a prototype of the cluster .
Applications of Clustering in different fields:
Marketing : It can be used to characterize & discover customer segments for marketing purposes.
Biology : It can be used for classification among different species of plants and animals.
Libraries : It is used in clustering different books on the basis of topics and information.
Insurance : It is used to acknowledge the customers, their policies and identifying the frauds.
City Planning: It is used to make groups of houses and to study their values based on their geographical locations and other factors present.
Earthquake studies: By learning the earthquake-affected areas we can determine the dangerous zones.
KNN Alogorithm